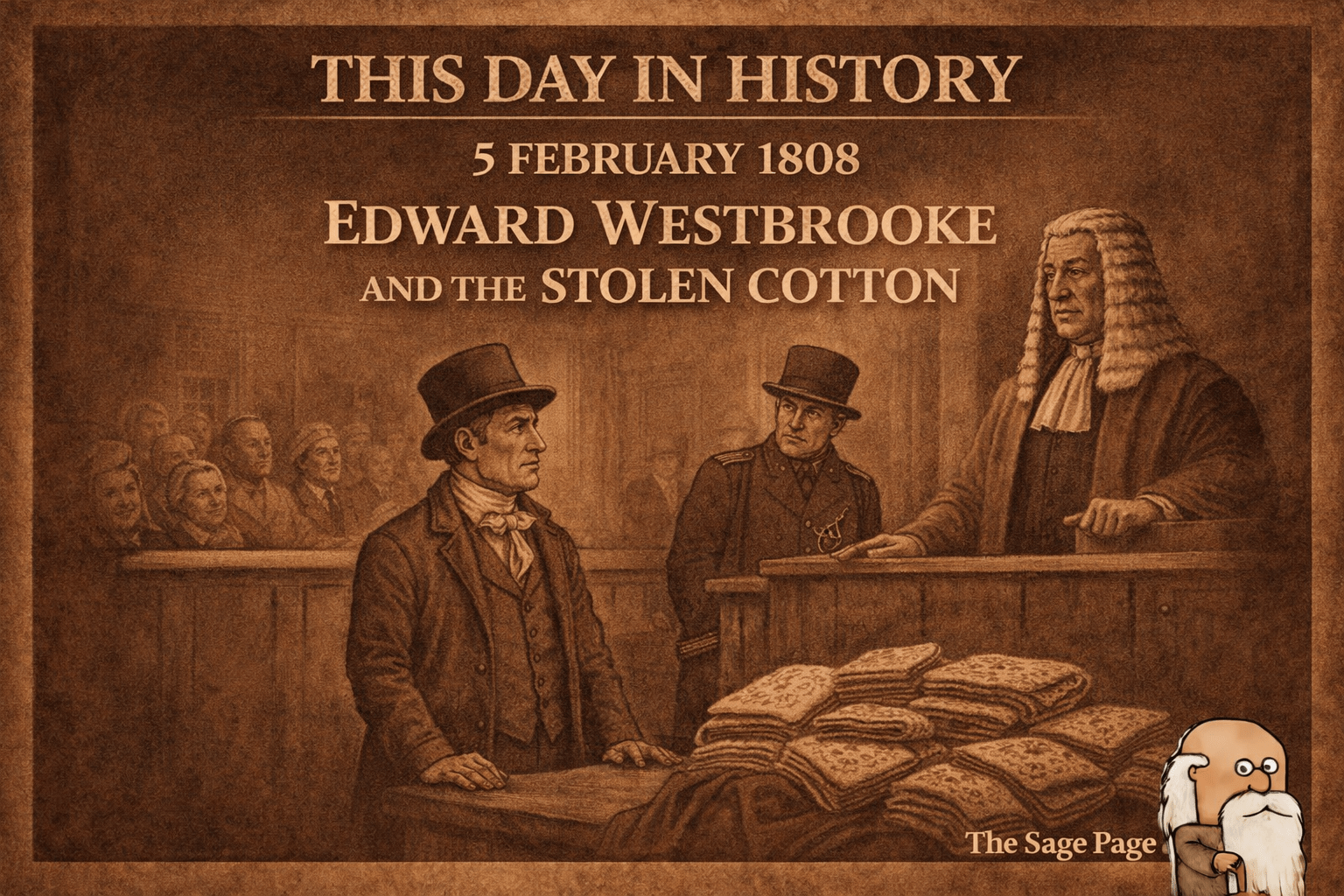On 11 March 1878 Fanny Roper Keech was convicted at the Old Bailey for fraud after obtaining costly costumes from Oxford Street silk mercers Gask and Gask using a worthless cheque and a false address. Her deception relied on confidence and appearance—but the cheque was quickly exposed as fraudulent.
Tag Archives: books
This Day in History – 6 March 1905
On 6 March 1905 Elizabeth Cove stood trial at the Old Bailey for wounding John Rubbins during a violent pub quarrel in Chalk Farm Road. The attack left the seventeen-year-old labourer permanently blinded in one eye. Despite the injury, the jury accepted the defence of self-protection and acquitted Cove.
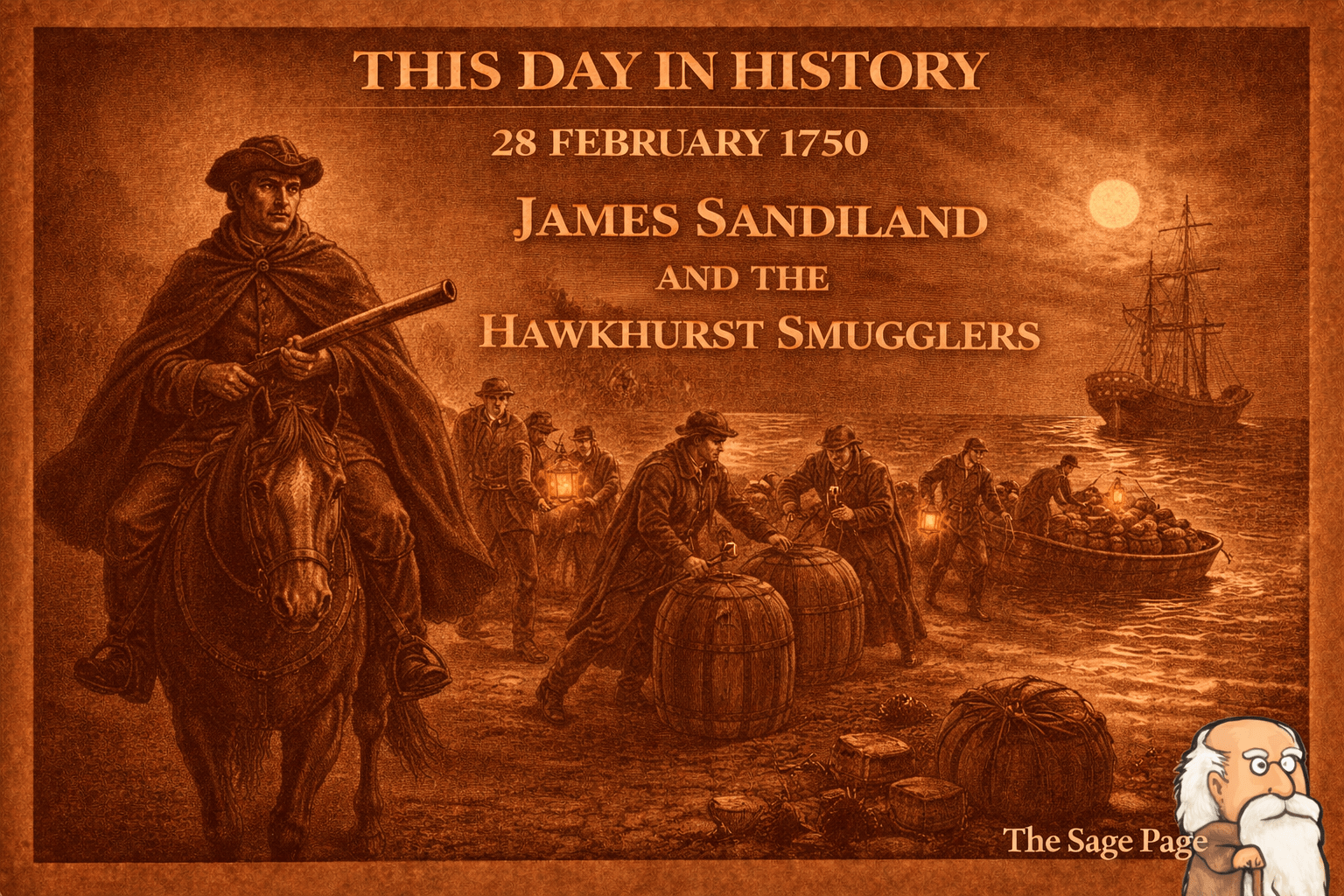
This Day in History – 28 February 1750
On 28 February 1750, James Sandiland was convicted at the Old Bailey for aiding armed smugglers of the Hawkhurst Gang in Kent. Despite claiming to be a respectable butcher, he was sentenced to death and executed at Tyburn for his role in landing untaxed tea and brandy.
This Day in History – 27 February 1843
In 1843, William Cannell shot barmaid Elizabeth Sarah Magness at the Auction Mart Hotel in Bartholomew Lane. Surviving both the attack and his own suicide attempt, Cannell was transported to Tasmania for fifteen years, where he later married and received a conditional pardon
This Day in History: 25 February 1784 — John Smith and the Harley Street Robbery
On 25 February 1784, John Smith was convicted at the Old Bailey for robbing Francis Franco at pistol-point in Harley Street. Though sentenced to death for stealing over sixty pounds in gold and a watch, his sentence was commuted, and he was transported to America for seven years.
This Day in History: 21 February 1787 — Charles Shaw and the Robbery at St Paul’s
On 21 February 1787, Charles Shaw was tried at the Old Bailey for robbing John Hughes near St Paul’s Churchyard. Accused of tripping him and stealing a silver watch worth forty shillings, Shaw was found guilty of highway robbery and executed at Newgate Prison on 26 April 1787.
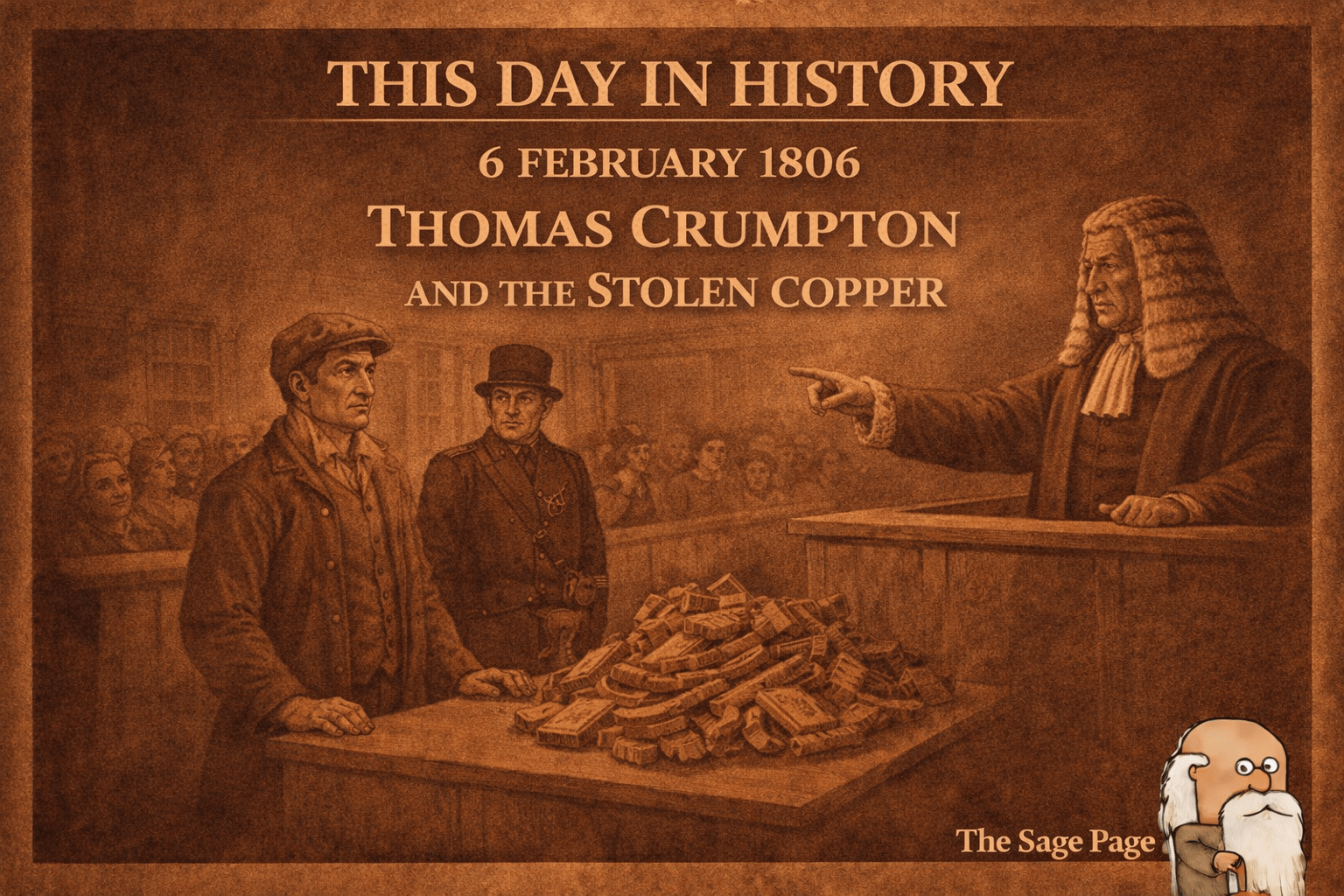
This Day in History: 6 February 1806 — Thomas Crumpton and the Stolen Copper
On 6 February 1806, Thomas Crumpton stood trial at the Old Bailey for stealing copper and metal goods worth just over a pound. Found guilty, he was sentenced to twelve months in the House of Correction and fined one shilling, highlighting how minor thefts were punished in Georgian London.
This Day in History: 5 February 1808 — Edward Westbrooke and the Stolen Cotton
On 5 February 1808, London’s highest criminal court, the Old Bailey, heard the case of Edward Westbrooke, who stood accused of stealing hundreds of printed cotton handkerchiefs and other textiles — goods of considerable value in the commercial heart of Georgian England. His trial, conviction and ultimate fate reveal much about how property, punishment andContinue reading “This Day in History: 5 February 1808 — Edward Westbrooke and the Stolen Cotton”
This Day in History: 29 January 1695 — Jeane Bates and the Stolen Plate
On 29 January 1695, Jeane Bates, using a false name, stole silver plate and household goods from her employer Peter Courtney. Tried at the Old Bailey, she was identified as a repeat offender, found guilty of felony, falsely claimed pregnancy, and was executed at Tyburn. Her case reveals the harsh punishment for servant theft in seventeenth-century London.
This Day in History: 27 January 1688 — Mary Aubry and the Dismembered Murder
On 27 January 1688, French midwife Mary Aubry murdered her abusive husband in London and dismembered his body. Tried at the Old Bailey on 22 February, she pleaded guilty and was sentenced to burning at the stake, carried out at Leicester Fields on 2 March 1688. Her case became one of early modern England’s most notorious.